Due to Zika virus, more than 1,600 babies were born in Brazil with microcephaly, or abnormally small heads, from September 2015 through April 2016. The epidemic took health professionals by surprise because the virus had been known since 1947 and was not linked to birth defects.
As scientists scrambled to figure out what was going on, one fact stood out: 83% of microcephaly cases came from northeastern Brazil, even though Zika infections were recorded nationwide.
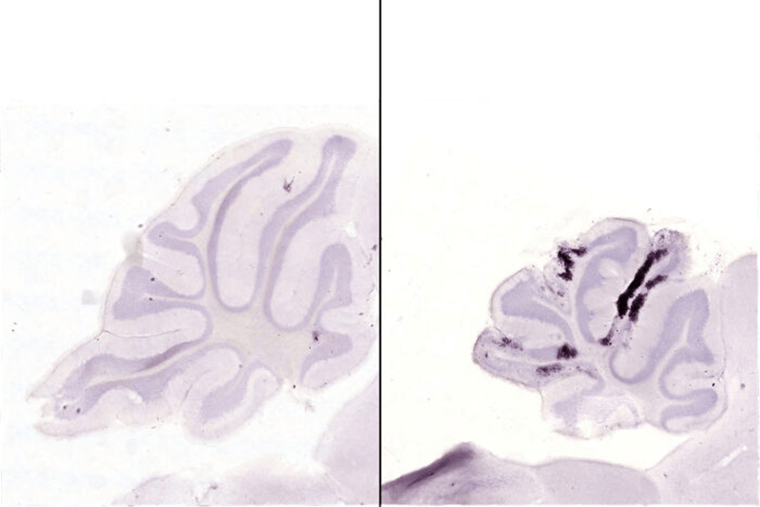
Researchers from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis since have learned that the strain of virus circulating in the northeastern Brazilian state of Paraíba in 2015 was particularly damaging to the developing brain. Kevin Noguchi, assistant professor of psychiatry and the study’s senior author, spoke about the findings, which are available online in The Journal of Neuroscience.
How did you determine that the Paraíba strain was unusually harmful?
We studied two strains of Zika virus — one from an outbreak in French Polynesia in 2013 that was associated with a low risk of microcephaly, and another from Paraíba in 2015. We infected one group of newborn mouse pups with one strain and a second group with the other strain. The brains of newborn mice are at a similar stage of development to a second-trimester human fetus, when Zika virus causes considerable damage. Each strain led to about the same number of deaths, but the brain damage in the surviving mice was dramatically different. The mice infected with the French Polynesian strain seemed to successfully fight off the infection within about two weeks after infection, and we did not see any additional signs of damage after that. In contrast, we saw neurodegeneration in the mice infected with the Paraíba strain up to 30 days later, and they had smaller brains.